Automobile clutch and its components - An automobile has to operate under varying load conditions on the road. It may be noted that when starting engines and also during gear changes, it is necessary to cut off load upon the engine. The clutch is a device to continue or discontinue load on the engine as necessary to solve these problems.
The clutch is installed between the engine and transmission. It transmits the power of the engine generally through the use of friction. The clutch is linked to the clutch pedal in the passenger compartment. When the driver presses down on the clutch pedal, the linkages cause the clutch to disengage. This uncouples the engine from the transmission. When the driver releases the clutch pedal, springs in the clutch causes it to engage again. Now power can flow from the engine, through the clutch, to the transmission and power train.
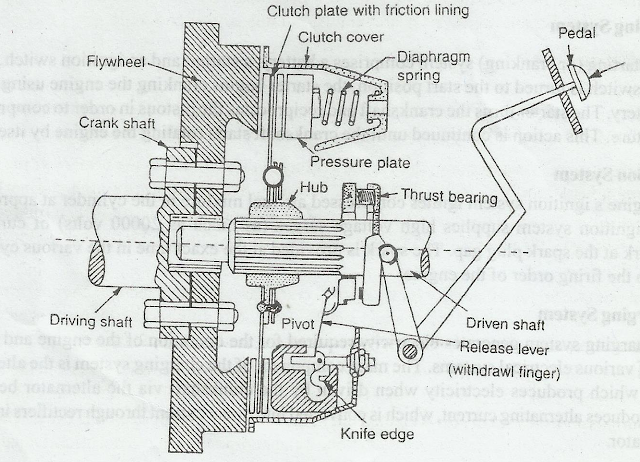
The main components of a clutch are engine flywheel, a friction (clutch) disc, and a pressure plate. The flywheel is connected to the engine crankshaft. When the engine is running, the flywheel is rotating. The pressure plate is attached to the flywheel and thus it also rotates. The friction disc, which is splined to transmission main shaft, is located between the two.
When the clutch pedal is in the released condition (i.e. when the clutch is engaged), the pressure plate is pushed solidly in direction of the flywheel by the diaphragm spring, which is located inside the clutch cover. This action binds the friction disc between the two driving members. These three components then rotate as one, allowing the rotation of the engine to be transferred to the transmission as shown in Figure above.
When the driver depresses the clutch pedal (to disengage the clutch), the motion of the pedal is transferred using either hydraulic pressure or a cable to the release fork. The release fork then moves the release bearing, pushing it against the center of the diaphragm spring. This action forces the pressure plate to move away from the friction disc. There are now air gaps between the flywheel and the friction disc, and between the friction disc and the pressure plate. No power can be transmitted through the clutch.




No comments:
Post a Comment